We (The Next Organization) had the opportunity to speak at the European Association Summit (EAS) on April 22nd, 2021 about ‘How to design a future proof (post-covid) business model’.
A future proof business model is a business model that continuously creates, delivers and captures value, prepared to withstand future developments in the changing context. The business model describes the value that an organization offers to different customers. It outlines the capabilities and partners needed to create, market and deliver the value to generate the highest and most sustainable revenue streams possible. The business model is different from an earnings model. The business model describes the entire organization including proposition, customers, partners and earnings model. Therefore, an earnings model is part of a business model and describes the revenue structure of the products and/or services.
Back to the core in a new context
To stay relevant as an organisation, you should evaluate what the core of your business means in today’s context. What is the core? What is the reason for existing, the core purpose? How does your organisation express itself and what is the offer to today’s world? The core is identity, it determines values and inspires. It gives direction, support and helps to stay close to yourself, especially in difficult times. Therefore, your core must be a part of every decision you make or every action you perform.
What does this mean for an organisation? In these times of major change, take back on the Why and put it in the new context to reinvent the How and the What.

Why do we do what we do?
Conviction & meaning of the organisation
How do we do it?
How the organisation gets things done
What do we do?
The key activities of the organization
Trends and developments as a source of inspiration
It is important to go back to the Why, the meaning of the organization, in the new context. However, what is the new context? Trends and developments can be used as a source of inspiration to design what the new context may look like. For an organization, it can be interesting to look at three different types of trends and developments namely, Global societal trends, disruptive technology trends and market-specific trends.
After you identified the relevant trends and developments, the trends and developments can be used to challenge the business model of the organization. What does it imply? First to keep a close eye on the ongoing and future trends and developments. Second to translate these trends and developments into the impact on customer behaviour and interaction. And next how this behaviour and interaction of customers influence the business model of the organization.
The Future of customer interaction is a model to understand social interaction and define impact on business models in all different industries.

Key elements to make a business model future proof
Key elements are the basis of a sustainable business model requested by the market. Elements for a sustainable business model can be different for each company and change over time. Despite this, several key elements apply as preconditions for establishing a sustainable business model, namely:
• Values and norms
• Social and ecologic responsibility
• Diversity and inclusion
• Customer centricity
• Being connected to all stakeholders
• Anticipation on market dynamics/context
• Digitization & data-driven
• Modularity and agility
The most important lesson is to stay awake as an organization. The biggest risk for companies is to stick to an outdated business model.
Major paradigm shifts
When designing a sustainable business model as an organization you need to take three major paradigm shifts into account
The focus on the ‘value in use’ of value propositions
Value in use takes the perspective of value from the customers point of true value from the customer’s point of view. This value is created while using the products or services from a provider. This is the point of departure designing value propositions and customer experiences.
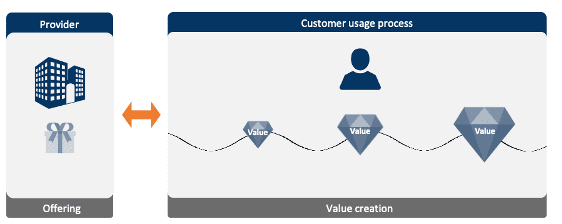
A tool to measure the value in use is VALEX. VALEX is the customer-centric index that creates insight into the customer’s value experience (what and how customers experience/ perceive) for different offerings in every step of their journey.
The value chains, from pipelines to platforms in networks
As technology is becoming a bigger part of society new methods of doing business pop up. One of the leading trends over the past years is the creation of online platforms or so-called communities. They support an already existing interaction or create new forms of interaction.
One of the most important aspects of the definition “platform” is this: it’s not just technology, but it is a new business model mainly focussed on sustaining interactions. However, what is exactly the difference between a pipeline and a platform business model (BM)? A pipeline business model is a market focused on consumer, where the platform BM is focused on producer and consumer. Secondly, the pipeline BM has a competitive advantage through means where the platform BM has the advantage through an ecosystem. Further, the value creations in the pipeline BM is created through the process and in the platform BM through the interaction of the community. Therefore, the power of the platform is the smart combination of technology, connectivity and data.
The focus on sustainability among others circularity
In the world of today, an organization has to recognize and anticipate, therefore COVID-19 can be seen as an exercise. For example, the traditional marketing P’s are make place for the three S’s and the four R’s concerning sustainability (based on the work of prof. dr. Peter Leeflang).

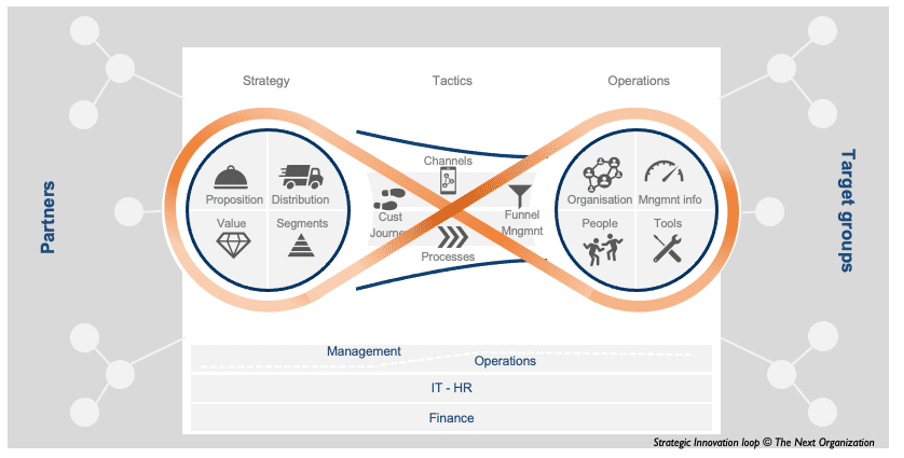
Businessmodel framework
The rapidly changing world demands agility from organisations. The rhythm of the organisation must be a continuous cycle of strategy and agility, the strategic innovation loop for continuous improvement. Changes in the context must be taken into account each time.
• Periodically, by looking at trends and developments and translating them into relevant sustainability of the business model.
• Continuously, by being in constant dialogue with target groups, partners and the various disciplines within the organisation.
Make the transformation happen
Last but not least. Make the transformation happen. Therefore you have to identify building blocks for a sustainable roadmap. There are seven topics for a successful transformation (based on theory and practice).
The next context for transformation
• What do we mean by transformation?
• What is the ‘purpose’ and are the (social) objectives?
• The new context
• A moving dot on the horizon
Propositions in the new context
• Developments in the sector
• Propositions in the new context
• Business model innovation
• Market approach and operation
Transformation capacity of the organization
• Continue to anticipate
• Be focused and flexible
• The organisation’s capacity for change
Transformation principles
• A rhythm of continuous proactive and reactive development
• The individual, group and organisational level
• Principles of transformation
• Success factors
Realising transformation
• Change methodologies
• How change works in the internal and external network
• From strategy to operations, including the organisation, IT and people
Scenarios and finances
• Scenarios
• The business case for transformation
• Financial planning
Leading change
• Leading the change
• Competencies, skills and success factors
• Financial management and business case



